SBC SIP中继配置
SBC - SIP Trunking
The SIP trunking use case is typically when you place the SBC between the PBX and the ITSP. This same use case would apply when joining two ITSPs together. The SBC in this use case is really being used as the SIP demarcation point between the internal network and the external network. The SBC also provides greater interoperability between the two networks as well as security.
IP Addresses
IPPBX IP: 192.168.1.10
ITSP FQDN: sbc.sangoma.com
SBC LAN IP: 192.168.1.20
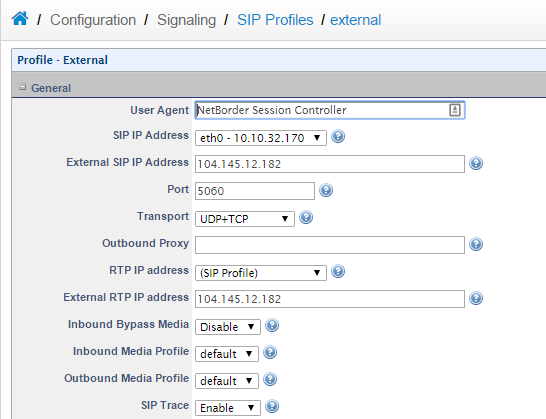
SBC DMZ IP: 10.10.4.106
SBC Public IP: 104.145.12.182
The SBC is acting as a SIP firewall in this case, where all the external SIP traffic passes through the SBC to the IPPBX. The SBC's DMZ IP address will either have 1-to-1 NAT setup or port forwarding from a fixed public IP address.
- 1. Network Setup
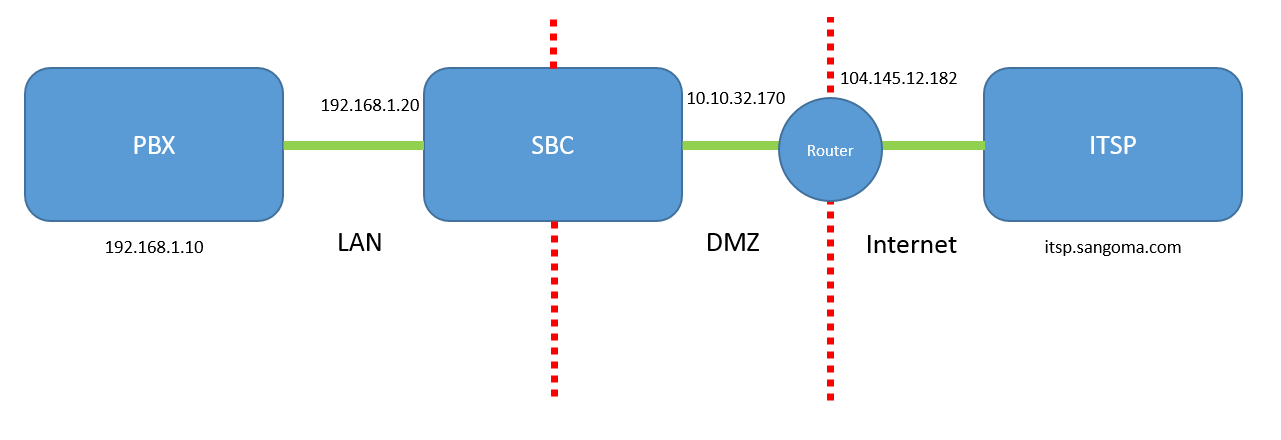
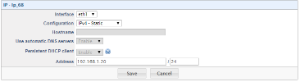
a. Login to the SBC (Configuraiton > IP Settings > Network > IP)
b. Set IP addresses of both eth0 and eth1.
c. Go to > IP tab > Add > Interface (eth0/eth1) > for eth0 we have assigned the DMZ IP 10.10.4.106, and for eth1 we have assigned the LAN IP 192.168.1.20
d. Next configure the default gateway and DNS servers.
Note: The default gateway is in the DMZ network to ensure all traffic for the ITSP leaves from the DMZ public IP address. If this the default gateway is set to the LAN gateway this can introduce audio issues.
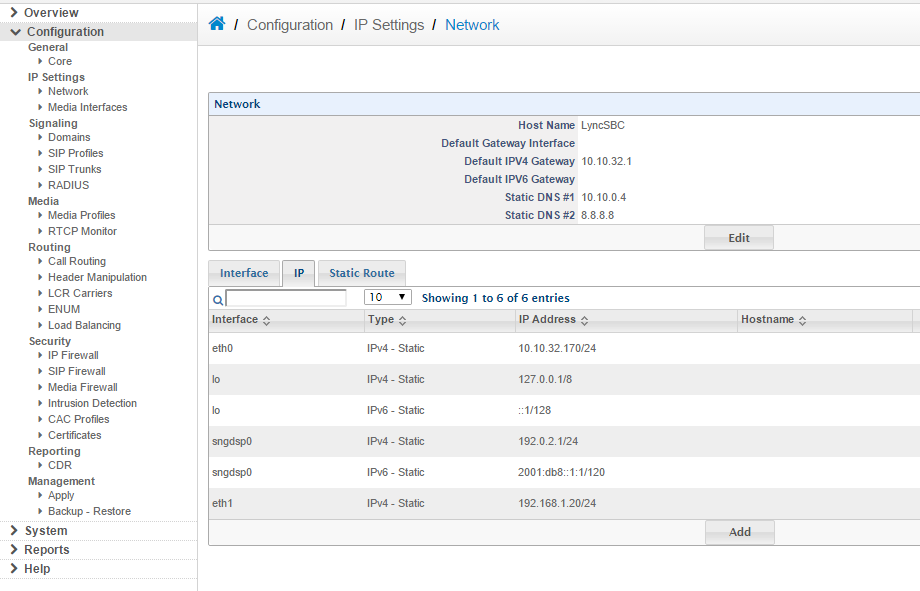
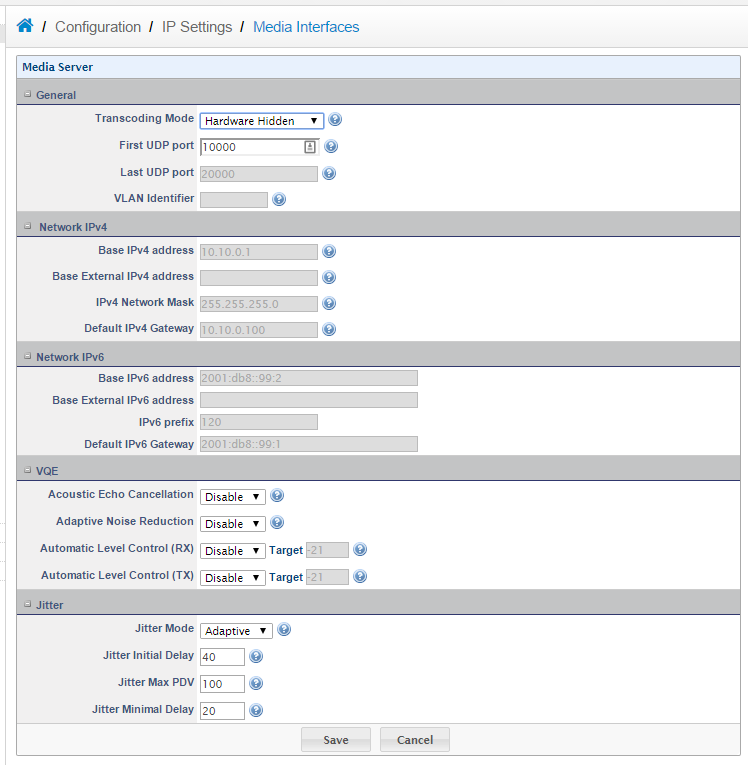
e.Next detect the media interfaces by going to Configuration > IP Settings > Media Interfaces and clicking edit. On the next screen simply click save to do the detection.
f. Then when the media interface is detected you will see the output below:
- 2. SIP Profile
We will create the External SIP Profile using the DMZ IP address, and then the Internal SIP Profile using the LAN IP address.
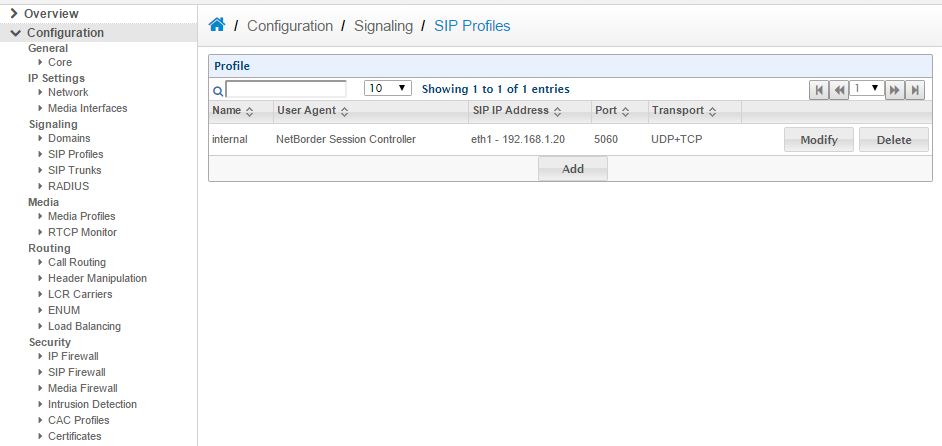
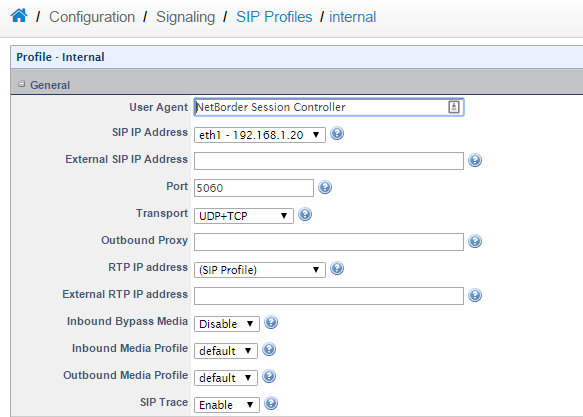
a. Goto > Configuration > Signaling > SIP Profiles then click Add and name the SIP profile Internal.
b. Set the SIP IP Address to 192.168.1.20 c. Enable SIP tracing. (Useful for debugging call issues)
d. Do exactly the same procedure but for External SIP Profile
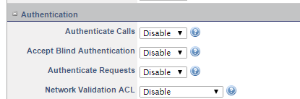
e. The only extra action that we need to ensure, is that the Authenticate Calls option is DISABLED if we don't have users registering TO or THROUGH the SBC.
- 3. SIP Trunks
The next step would be to create SIP trunks. a. The first Trunk would be facing the ITSP, and therefore we'd call it ITSP. b. Goto > Configuration > Signaling > SIP Trunks > Add > name it: ITSP c. Then assuming that we do not register to the ITSP:

d. In case that we do register to the ITSP, then we'd set up this as follows:

e. Then we'd need to create a second SIP Trunk that would face the PBX, so we name it - PBX f. Goto > Configuration > Signaling > SIP Trunks > Add > name it: PBX
 And this is the complete status that shows both SIP Trunks:
And this is the complete status that shows both SIP Trunks:

- 4. Call Routing
a. The next step is the call routing. Goto > Configuration > Routing > Call Routing > Add > Name it: External (We name it exactly as a SIP PRofile, so it won't be confusing ) b. The first rule that we want to add is the Security rule, so me make sure that the call is coming only from the ITSP c. In addition we'd need to know the IP of the ITSP. If we don't know the IP, we can simply obtain it by using the "nslookup" command in the CMD. (Example: nslookup sangoma.com, shows us 50.56.194.118)
 Then after the Submit, the dial rule would look like:
Then after the Submit, the dial rule would look like:
 d. The next rule would be to route the call from ITSP to the PBX. So we add a new rule:
d. The next rule would be to route the call from ITSP to the PBX. So we add a new rule:

NOTE: In some cases the REFER handling is required. Please review the folowing tutorial: NSC-SIP-Refer-Handling
This is the complete picture after we done with the External dial rules:
 e. Then we'd need to create a dial rule for the other direction. Goto > Configuration > Routing > Call Routing > Add > Name it: Internal
f. To simplify the process, we can copy the content of the rule from the External, as follows:
e. Then we'd need to create a dial rule for the other direction. Goto > Configuration > Routing > Call Routing > Add > Name it: Internal
f. To simplify the process, we can copy the content of the rule from the External, as follows:
 g. We change the name from External to Internal and mak a copy from External, because it's very similatr logic. Then we only change the IPs
g. We change the name from External to Internal and mak a copy from External, because it's very similatr logic. Then we only change the IPs
 h. And then we change the Bridge to Trunk destination from PBX, to the ITSP:
h. And then we change the Bridge to Trunk destination from PBX, to the ITSP:

- 5. Binding the Call Route to SIP Profile
a. The next step would be to take the Dial Rule and bind it to SIP Profile. Goto > Configuration > Signaling > SIP Profiles > Internal > Modify > Edit

b. Then we just change the Routing Plan dropdown section to Internal

c. Then repeat the exact same procedure for the External.

At this point the SBC is pretty much configured. Customer can start making calls to test, and if everything is about right, he can enable more security features.
- 6. Enabling the Intrusion Detection
If everything works well until this moment, we would proceed with enabling the Intrusion Detection. a. Goto > Configuration > Security > Intrusion Detection, and then check ON evertyhing as follows:

b. Then you go to Overview > Dashboard > Control Panel > Configure and Apply all the Configuration.

- 7. Firewall
a. The next thing that worth to check is the firewall. Goto > Configuration > Security > IP Firewall. We have SIP port, and some management ports added by default. RTP ports are absent. They will be added on the fly as the call goes.

b.Make sure that the SIP port and the RTP ports are forwarded in the router. To find out the range of the RTP ports, simply Goto > Configuration > Ip Settings > Media Interfaces, and as we can see the range is 10000-13999

- 8. Starting Services
The configuration is complete. The last and only step is to start all the services in the SBC. Goto > Overview > Dashboard > Control Panel Then start all the relevant services: Vega Session Controller, Instrusion Detection, Intrusion Prevention, Firewall , Secure Shell.